Temperature measurement
Describe the methods of temperature measurement
Non-electrical thermometers (2 liquids and 2 metals)
- liquid thermometer (e.g. mercury, alcohol)
- liquid crystal
- bourdon gauge
- bimetallic strip
Electrical (FIR TTT)
- fibre-optic
- infrared
- resistance thermometer
- thermistor
- thermocouples
- thermopiles
Thermometer type | Description (principle, pros & cons) |
|---|---|
Liquid thermometer | Heating causes thermometric fluid (e.g. mercury or alcohol) to expand. Increased volume is measured as height of a column calibrated to temperature. Pros: Cheap, no power required, reliable, no calibration.
|
Bourdon gauge thermometer | Thermal expansion of fluid pushes a spiral metal tube which unwinds and moves a pointer on a calibrated scale. Pros: Cheap, no power required, less invasive. 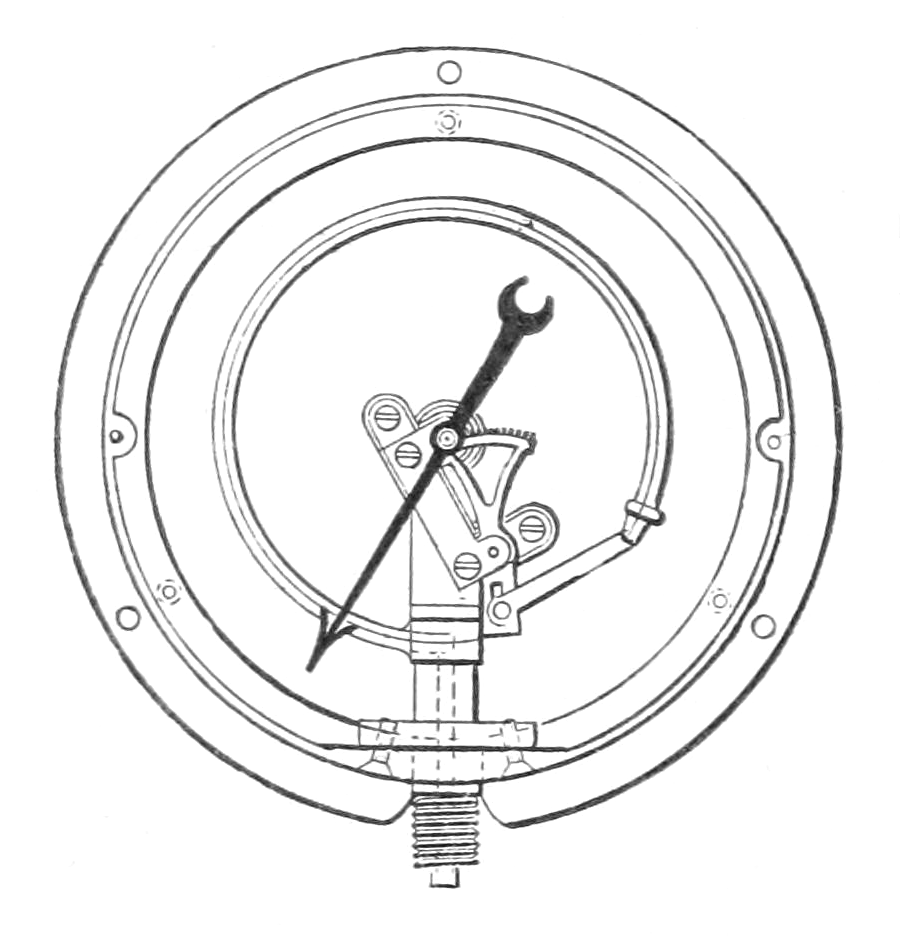 |
Bimetallic strip thermometer | Two bonded metal strips (e.g. copper and steel) expand at different rates, causing them to bend. The degree of curvature is calibrated to temperature. Pros: Cheap, no power required.
|
Liquid crystal thermometer | Liquid crystals change colour with temperature. The colour is compared with a calibrated scale. Pros: Cheap, no power required |
Infrared thermometer | Measures electromagnetic radiation emitted by the body, which is within the infrared spectrum. Higher temperature → higher frequency radiation. Pros: Non-invasive, sensitive. |
Thermocouple | Relies on the Seebeck effect: a voltage develops at the junction of two different metals and varies predictably with temperature Pros: Rapid and reliable over a broad range of temperatures that far exceed what can be found in the human body.
|
Thermopile | Multiple thermocouples connected in series to increase sensitivity. Pros: Greater sensitivity. |
Resistance thermometer | Commonly made from platinum (platinum resistance thermometer). Electrical resistance in the wire increases with temperature; measured using a Wheatstone bridge and calibrated to temperature. Pros: Accurate, sensitive, minimal calibration drift. 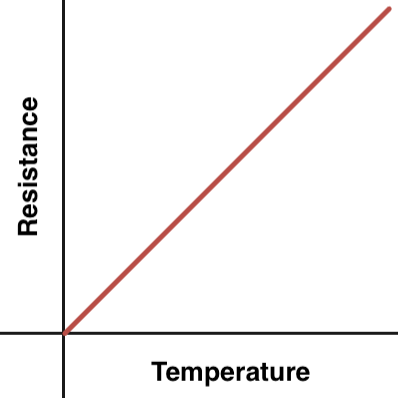
|
Thermistor | Electrical resistance of a semiconductor decreases with increasing temperature; measured using a Wheatstone bridge. Often used for temperature measurement and calculation of cardiac output (via thermodilution) in pulmonary artery catheters. Pros: Cheap, reliable, fast. 
|
Fibre-optic thermometry | Gallium–arsenic crystal at fibre tip absorbs light. The absorption spectrum varies with temperature. An illuminator transmits light to the crystal and the absorption spectrum is analysed by spectometry. Pros: Accurate in high electromagnetic interference environments (e.g. MRI). 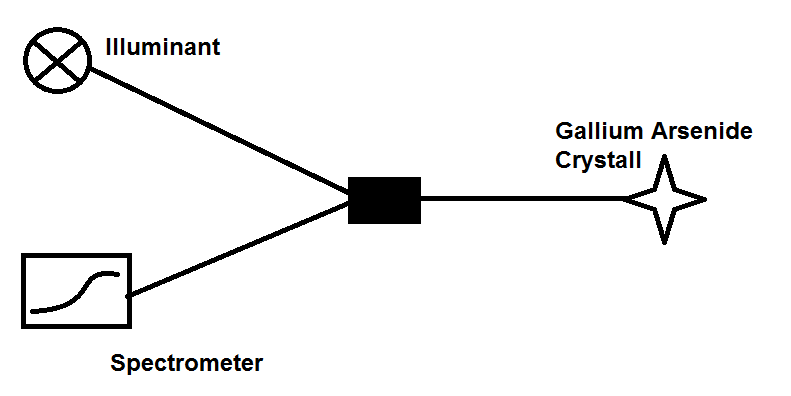
|


